소개

Prof. 오은규
E-mail: ekoh@korea.ac.kr
Hana Science Hall
Room #511 & 505
- Introduction
- About Professor
- Research
- Publication
- Lab Members
- Notice
Lab Opening
동물은 환경이 좋은 곳으로 이동을 할 수 있지만, 식물은 그렇지 못합니다. 생존과 번식을 위해서 식물은 반드시 주변 환경에 적응을 해야만 합니다. 따라서 식물은 끊임없이 변하는 환경에도 생존할 수 있도록 매우 다양한 방법을 개발했습니다. 본 연구실에서는 모델 식물인 애기장대 (Arabidopsis Thaliana) 시스템을 사용하여, 식물이 어떤 방법으로 주변 환경에 적응하는지를 분자 수준에서 밝히는 연구를 하고 있습니다.또한 최근에는 합성생물학 방법을 이용하여, 식물의 다양한 신호전달과정을 조절할 수 있는 분자 도구를 개발하고 있습니다. 만들어진 분자 도구를 이용하여 신호전달과정의 새로운 분자기작을 규명하고 있으며, 또한 실제 작물에 적용하여, 다양한 농업적 형질 (e.g., 생산성, 병저항성)이 향상된 작물을 개발하고 있습니다.
Professor
EDUCATION
2003.03 – 2008.02
1999.03 – 2003.02
M.S.-Ph.D. in Dept. of Biological Science, KAIST, Korea
Thesis: Functional roles of PIL5 in Arabidopsis seed germination
(Advisor: Prof. Giltsu Choi)
B.S. in Dept. of Biological Science, KAIST, Korea
PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE
2018.09 – present
Assistant Professor,
Division of Life Sciences,
Korea University. Korea
2016.03 – 2018.08
Assistant Professor,
Department of Bioenergy Science and Technology,
Chonnam National University. Korea
2009.11 – 2016.02
Postdoctoral Fellow,
Carnegie Institution for Science Department of Plant Biology
(Advisor: Dr. Zhiyong Wang)
2008.03 – 2009.10
Postdoctoral Fellow,
Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, Korea
(Advisor: Prof. Giltsu Choi)
2003.03 – 2008.02
Research and Teaching Assistant,
Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, Korea
Research
Research Topic
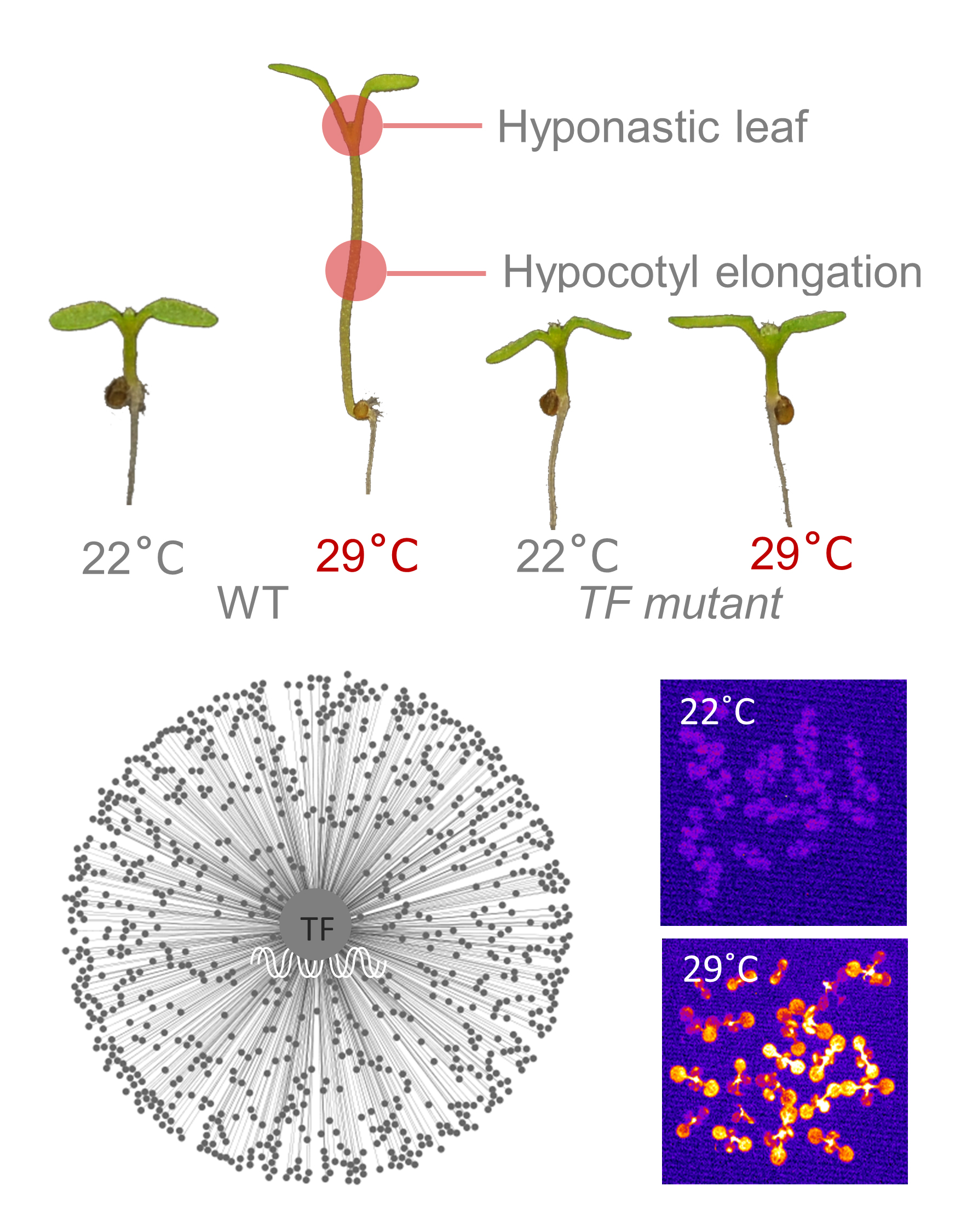
1. 식물 고온형태형성 신호전달 네트워크 규명
모델 식물인 애기장대는 형태적인 변화를 통해서 고온 스트레스에 적응을 합니다. 고온에 의한 식물의 형태적인 변화를 고온형태형성(thermomorphogenesis)이라고 부릅니다. 본 연구실은 고온형태형성을 모델 시스템으로 이용하여 식물이 어떻게 고온을 인지하며, 고온 스트레스에 적응하는지를 분자 수준에서 규명하는 연구를 진행하고 있습니다.
2. LRR-RK 신호전달 네트워크 규명
식물은 세포막에 존재하는 Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor Kinases (LRR-RKs)를 이용하여, 다양한 환경신호를 인지합니다. 그리고 인지된 화학신호는 복잡한 신호전달 과정을 거쳐서 식물의 발달 및 면역반응을 조절합니다. 현재 본 연구실에서 개발한 LRR-RK의 활성을 인위적으로 조절할 수 있는 분자도구를 이용하여, 애기장대에 존재하는 모든 LRR-RK의 생물학적 기능과 이들의 리간드를 규명하는 연구를 진행하고 있습니다.
3. 신호전달 재설계를 통한 작물 개량
이전의 식물-환경 상호작용의 연구를 통해서 얻은 유전학적 지식을 기반으로 작물의 신호전달을 재설계하면, 환경 스트레스에 내성을 지니거나, 형태 및 발달이 우수한 작물을 개발할 수 있습니다. 현재 CRISPR/Cas9 유전자편집 기술을 이용하여 토마토의 유전 정보를 편집하여 농업적으로 우수현 형질의 토마토를 개발하는 연구를 진행하고 있습니다.
Publications
26.
Pandey, S.K., Lee, H.W., Kim, M.J., Cho, C., Oh, E., and Kim, J. (2018). LBD18 uses a dual mode of a positive feedback loop to regulate ARF expression and transcriptional activity in Arabidopsis. Plant J 95:233-251.
25.
Oh, E.*, Seo, P.*, and Kim, J. (2018) Signaling Peptides and Receptors Coordinating Plant Root Development. Trends Plant Sci 23, 337-351
24.
Kim, S., Hwang, G., Lee, S., Zhu, J.Y., Paik, I., Nguyen, T.T., Kim, J., and Oh, E. (2017). High Ambient Temperature Represses Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Degradation of HY5. Front Plant Sci 8, 1787.
23.
Hwang, G., Zhu, J.Y., Lee, Y.K., Kim, S., Nguyen, T.T., Kim, J., and Oh, E. (2017). PIF4 Promotes Expression of LNG1 and LNG2 to Induce Thermomorphogenic Growth in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 8, 1320.
22.
Zhu, J.Y., Li, Y., Cao, D.M., Yang, H., Oh, E., Bi, Y., Zhu, S., and Wang, Z.Y. (2017). The F-box Protein KIB1 Mediates Brassinosteroid-Induced Inactivation and Degradation of GSK3-like Kinases in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 66, 648-657 e644.
21.
Zhu, J.Y.*, Oh, E.*,#, Wang T., and Wang, Z.Y.# (2016). TOC1–PIF4 interaction mediates the circadian gating of thermoresponsive growth in Arabidopsis. Nature communications 7, 13692 (*equal contribution;#co-corresponding author)
20.
Choi, H., and Oh, E. (2016). PIF4 Integrates Multiple Environmental and Hormonal Signals for Plant Growth Regulation in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 39, 587-593
19.
Jeong, J., Kim, K., Kim, ME., Kim, HG., Heo, GS., Park, OK., Park, Y., Choi, G. *, and Oh, E. * (2016) Phytochrome and Ethylene Signaling Integration in Arabidopsis Occurs via the Transcriptional Regulation of Genes Co-targeted by PIFs and EIN3. Front. Plant Sci. 7:1055. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01055 (*co-corresponding author)
18.
Chaiwanon, J., Wang, W., Zhu, J.Y., Oh, E., and Wang, Z.Y. (2016). Information Integration and Communication in Plant Growth Regulation. Cell 164, 1257-1268
17.
Oh, E.*, Zhu, J.Y.*, Ryu, H., Hwang, I., and Wang, Z.Y. (2014). TOPLESS mediates brassinosteroid-induced transcriptional repression through interaction with BZR1. Nature communications 5, 4140 (*equal contribution)
16.
Oh, E., Bai, M.Y., Zhu, J.Y., Arenhart, R., Sun, Y., and Wang, Z.Y. (2014). Cell elongation is controlled through a central molecular circuit in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. eLife 3:e03031.
* This article was highlighted in F1000 Prime (http://f1000.com/prime/718421656)
15.
Fan, M, Bai, M.Y, Kim, J., Oh, E., Park, C., Kim, S., and Wang, Z.Y. (2014). HBI1 mediates the tradeoff between growth and PAMP-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell 26, 828-841.
14.
Bai, M.Y., Fan, M., Oh, E., and Wang, Z.Y. (2012). A triple helix-loop-helix/basic helix-loop-helix cascade controls cell elongation downstream of multiple hormonal and environmental signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. The Plant cell 24, 4917-4929.
13.
Wang, Z.Y., Bai, M.Y., Oh, E., and Zhu, J.Y. (2012). Brassinosteroid signaling network and regulation of photomorphogenesis. Annual review of genetics 46, 701-724.
12.
Bai, M.Y., Shang, J.X., Oh, E., Fan, M., Bai, Y., Zentella, R., Sun, T.P., Wang, Z.Y. (2012) Brassinosteroid, gibberellin and phytochrome impinge on a common transcription module in Arabidopsis. Nature cell biology (Articles) 14, 810-817.
11.
Oh, E., Zhu, J.Y., Wang, Z.Y. (2012). Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses. Nature cell biology (Articles) 14, 802-809.
* This article was highlighted in F1000 Prime (http://f1000.com/prime/717953302)
10.
Hao, Y.*, Oh, E.*, Choi, G., Liang, Z., and Wang, Z.Y. (2012). Interactions between HLH and bHLH factors modulate light-regulated plant development. Molecular plant 5, 688-697. (*equal contribution).
9.
Sun, Y., Fan, X.Y., Cao, D.M., Tang, W., He, K., Zhu, J.Y., He, J.X., Bai, M.Y., Zhu, S., Oh, E., Patil, S., Kim, T.W., Ji, H., Wong, W.H., Rhee, S.Y., and Wang, Z.Y. (2010). Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 765-777.
8.
Luo, X.M., Lin, W.H., Zhu, S., Zhu, J.Y., Sun, Y., Fan, X.Y., Cheng, M., Hao, Y., Oh, E., Tian, M., Liu, L., Zhang, M., Xie, Q., Chong, K., and Wang, Z.Y. (2010) Integration of light- and brassinosteroid-signaling pathways by a GATA transcription factor in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 19, 872-883.
7.
Kang, H., Oh, E., Choi, G., and Lee, D. (2010) Genome-wide DNA-binding specificity of PIL5, an Arabidopsis basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor. International journal of data mining and bioinformatics 4, 588-599.
6.
Oh, E., Kang H., Yamaguchi S., Park J., Lee D., Kamiya Y., and Choi, G. (2009) Genome-Wide Analysis of Genes Targeted by PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 3–LIKE5 during Seed Germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 21, 403-419.
5.
Kim, D. Yamaguchi, S. Lim, S., Oh, E., Park, J., Hanada, A., Kamiya, Y., Choi, G. (2008) SOMNUS, a CCCH-type Zinc Finger Protein in Arabidopsis, Negatively Regulates Light-Dependent Seed Germination Downstream of PIL5. Plant Cell 20, 1260-1277
4.
Oh, E., Yamaguchi, S., Hu, J., Yusuke, J., Jung, B., Paik, I., Lee, H.-S., Sun, T.-p, Kamiya, Y., and Choi, G. (2007) PIL5, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH protein, regulates gibberellin responsiveness by directly binding to the GAI and RGA promoters in Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell, 19, 1192-1208.
3.
Oh, E., Yamaguchi, S., Kamiya, Y., Bae, G., Chung, W.-I., Choi, G. (2006) Light activates the degradation of PIL5 protein to promote seed germination through gibberellin in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 47, 124-139.
2.
Oh, E., Kim, J., Park, E., Kim, J-I, Kang, C., and Choi, G. (2004) PIL5, a phytochrome interacting basic helix-loop-helix protein, is a key negative regulator of seed germination in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16, 3045-3058.
1.
Park, E., Kim, J., Lee, Y., Shin, J., Oh, E., Chung, W.-I., Liu, J.R., and Choi, G. (2004) Degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3 in phytochrome-mediated light signaling. Plant Cell Physiol. 45, 968-975
Members
현재
#석박사통합
김사라
황건희
#석사
박정향
#연구원
서다인
과거
Thom Nguyen (석사)
이슬기(학부졸업연구)
Notice
함께 연구할 대학원생 (석박사통합 or 박사)을 모집하고 있습니다.
관심있는 분은 언제든지 ekoh@korea.ac.kr 로 연락주시기 바랍니다.
Links
Plant Gene Set Enrichment / GO analysis
http://structuralbiology.cau.edu.cn/PlantGSEA/
GO analysis_AgriGO
http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/index.php
Heatmap
http://www1.heatmapper.ca/expression/
Design of qRT-PCR primers
http://atrtprimer.kaist.ac.kr/
Multiple protein sequences alignment
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/muscle/
ePLANT
http://bar.utoronto.ca/eplant/
Tissue, specific expression similar to bar.
http://efp.ucr.edu/cgi-bin/relative.cgi
String - protein-protein interaction
Mapman
http://mapman.gabipd.org/web/guest
qPCR primer design
http://www.quantprime.de/?page=home
Scripture
http://www.broadinstitute.org/software/scripture/
lncRNA genome brower
http://chualab.rockefeller.edu/cgi-bin/gb2/gbrowse/arabidopsis/
Plant small RNA target finder
http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/
RNA secondary structure prediction
http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/RNAfold.cgi
Dnase-Seq
Brassica database
http://brassicadb.org/brad/index.php
Protein subcellular localization
http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/Cell-PLoc-2/
Circadian clock
http://diurnal.mocklerlab.org/
Positive / negative selection
NGS pipelines in UGENE
Arabidopsis bulk sequence download
http://www.arabidopsis.org/tools/bulk/sequences/index.jsp
CRISPR gRNA design
http://chopchop.cbu.uib.no/search.php
http://www.e-crisp.org/E-CRISP/index.html
Brassica rapa (Chiifu-401) genome database
Transmembrane domain prediction
http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/TMPRED_form.html
http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/
AlBERTO AraBidopsis Embryonic and Root Transcriptome brOwser
http://albertodb.org/#nav-start
Melting Curve Prediction
https://www.dna.utah.edu/umelt/um.php
Phylogenic tree generator
http://www.trex.uqam.ca/index.php?action=newick&project=trex
서로 다른 두 문장을 비교
PDF 변환
http://smallpdf.com/kr/excel-to-pdf
